Effects of rheologically stratified seawater during algal bloom on sinking dynamics of microplastics
Mrokowska M, Dzień K, Krztoń-Maziopa A, Water Research, 280, 123487, 2025
In this study, we investigated the previously unaddressed sinking dynamics of microplastics at the periphery of algal bloom regions in seawater. Our laboratory experiments involved a series of measurements in two-layered water columns, where the transition occurred between typical seawater and exopolymer-rich seawater, which can form during intensive algal blooms (e.g., mucilage events). Since exopolymers impart non-Newtonian properties to seawater, microplastics crossing the Newtonian-to-non-Newtonian transition exhibited significant variations in their sinking dynamics, including changes in settling velocity and orientation. As a result, particles tended to remain longer in this region, suggesting that the increased viscosity and viscoelasticity of bloom-affected areas may promote the accumulation of microplastics and enhance their interactions with the marine ecosystem.
Settling of microplastics in mucus-rich water column: The role of biologically modified rheology of seawater
Mrokowska M, Krztoń-Maziopa A, Science of the Total Environment 912, 168767, 2024
By combining hydrodynamic and rheological tests, we made a first step toward understanding how exopolymers secreted abundantly during algal blooms affect the sinking behaviour of microplastics, MP. In this study, we tested 15 types of MP including isometric (spheres and irregular particles) and anisometric (disks, rods, and blades) shapes to find that viscoelastic and shear-thinning properties of EPS-rich seawater completely modify sinking patterns of MPs compared to typical seawater. We identified decelerations, unsteady settling, orientation instabilities and tumbling motions of MPs. This study highlights the need to incorporate rheological effects in algal bloom-afflicted regions into MP transport models.

Effect of exopolymer gels on the viscoelasticity of mucus-rich saltwater and settling dynamics of particles
Mrokowska M, Krztoń-Maziopa A, Dębowski M, Marine Chemistry, 246, 104163, 2022
The structure of saltwater with gelatinous exopolymers secreted during algal blooms seriously affects the dynamics of fast-sinking marine particles. Here we addressed the effects of modified rheology of saltwater on marine sedimentation processes. Our tests revealed viscoelasticity of saltwater depends on polymer gel size. Settling experiments showed that saltwater with colloidal gels has a stronger inner structure and retards settling particles more effectively than saltwater with particulate gels. This suggests that exopolymer networks can form rheologically inhomogeneous structures in seawater, possibly inducing variation in the settling dynamics of particles, completely different from those known in typical seawater.

source: Mrokowska et. al 2024, Marine Chemistry, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marchem.2022.104163 under CC BY 4.0 licence
Viscoelastic and shear-thinning effects of aqueous exopolymer solution on disk and sphere settling
Mrokowska M, Krztoń-Maziopa A, Scientific Reports, 9, 7897, 2019
This study combined rheological measurements and settling experiments to demonstrate how shear-thinning and viscoelastic properties of xanthan gum solutions – models of exopolymer-rich natural water, affect the sinking of solid spheres and disks. The results quantified the dependence of average sinking dynamics on the concentration of XG and particle size and identified negative wakes behind particles. Findings are relevant in environmental sciences to facilitate the assessment of sedimentation processes and in technology and engineering related to particle-laden non-Newtonian fluids.
Conditions for homoaggregation of pristine polystyrene microplastic in aquatic environments
Lempart-Drozd M, Mrokowska M, Zych Ł, Goleń J, Krztoń-Maziopa A, Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 715, 136674, 2025
This study examined the homoaggregation of polystyrene microplastics in water with varying ionic strength, focusing on processes in the hydro-environment. The results indicated that aggregation was primarily driven by physical processes related to hydrophobicity, irregular shape, rough morphology, and hydrodynamic conditions. Settling tests revealed that homoaggregates maintained their integrity while sinking in solutions with a vertical gradient of ionic strength. This study provides valuable laboratory observations that contribute to research on plastics and their environmental processes.
Sinking behaviour of particles affected by density stratification:
Influence of pycnocline on settling behaviour of non-spherical particle and wake evolution
Mrokowska M, Scientific Reports, 10, 20595, 2020
Dynamics of thin disk settling in two-layered fluid with density transition
Mrokowska M, Acta Geophysica, 68, 1145-1160, 2020
Stratification-induced reorientation of disk settling through ambient density transition
Mrokowska M, Scientific Reports, 8, 412, 2018
In a series of lab experiments, I have studied the sinking of non-spherical particles in a stratified fluid to address delayed settling at density transitions in marine environments. I provided the first experimental evidence of stratification-induced reorientation of non-spherical particles. I identified phases of variations of settling velocity and particle orientation instabilities and demonstrated interactions between stratified fluid and wake evolution behind sinking disk. These findings are useful in explaining the dynamics of marine particles (mineral grains, microplastics, faecal pellets) in marine stratified systems and the motion of solid particles in engineering processes.
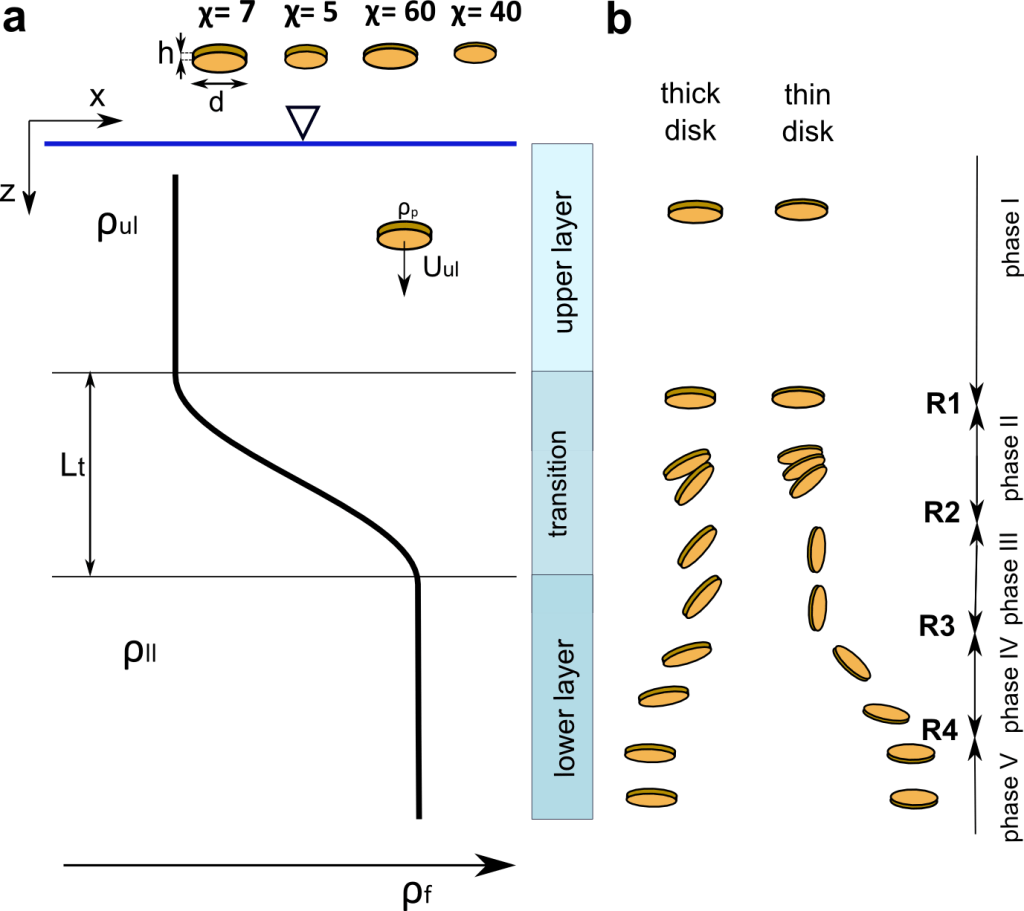
source: Mrokowska 2020, Scientific Reports https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-77682-y under CC BY 4.0 licence
Selected conference speeches
- 2024: Annual European Rheology Conference: Particles sinking in non-Newtonian seawater: the role of exopolymers in modifying sedimentation processes (Mrokowska M, Chabło T, Krztoń-Maziopa A), Leeds, UK
- 2023: Polish Congress of Rheology: Impact of rheological properties of xanthan gum/kappa-carrageenan dispersions in seawater on settling dynamics of solid particles (Mrokowska M, Dzień K, Krztoń-Maziopa A), Wieliczka, Poland
- 2022: Ocean Sciences Meeting: Effects of dispersed exopolymer gels on the rheology of water column and settling dynamics of solid particles: a laboratory perspective (Mrokowska M, Krztoń-Maziopa A, Dębowski M), online
- 2022: MICRO 2022 Effects of biologically modified seawater on settling behaviour of microplastics (Mrokowska M, Krztoń-Maziopa A), online
- 2022: IUTAM Symposium on “Particles, Drops and Bubbles in Stratified Environments”: Dynamics of disk settling in two-layered liquid with non-linear density transition (Mrokowska M), hybrid, Toulouse, France
- 2021: ASLO 2021 Aquatic Sciences Virtual Meeting: Effects of stratification and dissolved exopolymers on settling dynamics of solid particles in relation to mechanisms of marine snow formation (Mrokowska M, Krztoń-Maziopa A), online